Trees Birds Mammals Fish Amphibians Reptiles
Wild Algarve
Bookshop
Phallus hadriani Vent. - Dune Stinkhorn
Phylum: Basidiomycota - Class: Agaricomycetes - Order: Phallales - Family: Phallaceae
Distribution - Taxonomic History - Etymology - Toxicity - Identification - Reference Sources
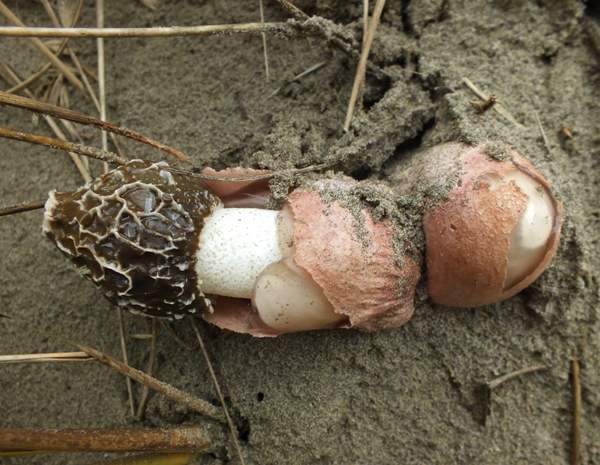

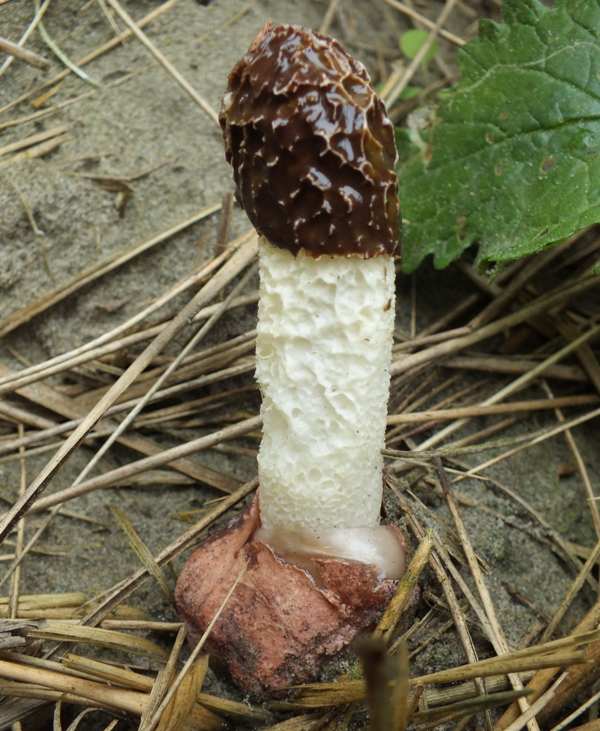
Phallus hadriani, the Dune Stinkhorn, emerges from an 'egg'
beneath the surface. The cap is initially covered with olive-green 'gleba',
a smelly coating that attracts insects which in turn distribute the spores. In Britain this is a rare species and almost exclusively restricted to sand dunes. A violet volva distinguishes the Dune Stinkhorn from the much more common Stinkhorn, Phallus impudicus, which has a white volva but in other macroscopic characteristics is much the same.

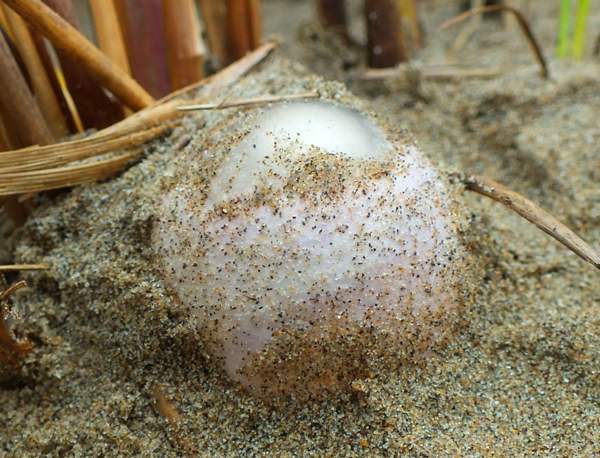
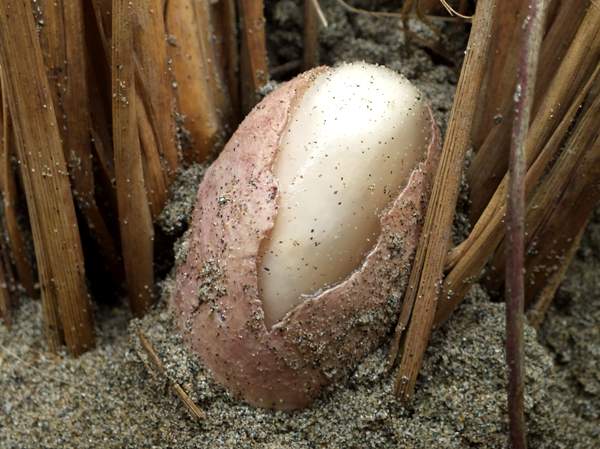
Even at the egg stage, a pinkish tinge differentiates the Dune Stinkhorn from the more common and widespread Stinkhorn Phallus impudicus, which has a white volva. The Dune Stinkhorn egg seen below was found in a coastal location in West Wales.

Distribution
Rather a rare find in Britain and Ireland, where it is largely confined to coastal sand dunes, Phallus hadriani also occurs in coastal zones and some dry inland regions of other countries in Europe, from Scandinavia to the southernmost parts of the Iberian Peninsula and the shores of the Mediterranean.
This species is also found in parts of Asia and North America. The Dune Stinkhorn is thought to be an introduced species in Australia.
Taxonomic history
The Dune Stinkhorn, Phallus hadriani, was described in 1798 by French botanist Étienne Pierre Ventenat (1757 - 1808), who gave it the scientific name Phallus hadriani (a binomial name that was subsequently sanctioned by Christiaan Hendrik Persoon in his Synopsis Methodica Fungorum of 1801).
Synonyms of Phallus hadriani include Phallus iosmus Berk., Hymenophallus hadriani (Vent.) Nees, and Phallus imperialis Schulzer.

Etymology
The genus name Phallus was chosen by Carl Linnaeus, and it is a reference to the phallic appearance of many of the fruitbodies within this fungal group.
The specific epithet hadriani is named in honour of Dutch botanist Hadrianus Junius (1512 - 1575) who, in 1564, wrote a pamphlet about stinkhorn fungi.
Toxicity
The vile smell of most mature stinkhorn fungi, and certainly Phallus hadriani, might be taken to suggest that these fungi are toxic or at least inedible; however, some people do eat them, but only at the 'egg' stage when the odour is not so evident. That said, I have heard of no instances of turf wars (or sand dune wars) over the rights to gather these edible but hardly delectable fungi. When fully mature, Dune Stinkhorns are greatly valued as
a source of food... by flies!
Identification guide
 |
Description
The 'egg' from which the Dune Stinkhorn emerges is typically 4 to 6cm in diameter,
gradually vertically becoming elongated until it ruptures and the stem emerges
quickly (usually taking little more than an hour to reach its maximum height), bearing the gleba-coated cap aloft.
Beneath the sticky olive-green gleba coating,
the cap of the Dune Stinkhorn has a raised honeycomb structure. This is
all that many people ever see of the cap of this fungus because insects
very quickly eat the spore-bearing gleba, at the same time getting some of
it stuck to their legs so that spores are transported over quite large
distances as the insects fly off in search of food elsewhere.
These stinkhorns range from 10 to 18cm tall; stipe diameter is 2 to 3.5cm; the caps vary from 2.5 to 4.5cm
across. |
 |
Stem and volva
The stem is white and looks like expanded polystyrene, and it emerges from the remains of a violet-coloured universal veil that covered the fruitbody at the egg stage and ultimately remains around the base of the stem like a bag.
After the gleba has been consumed by insects, the white stipes can
persist for several days, and so you can expect to see many more Dune Stinkhorns with white caps than with olive green ones. |
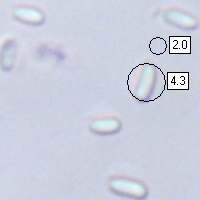 |
Spores
Oblong-ellipsoidal, smooth, 3-4.5 x 1.5-2.5µm.
Spore colour
Greyish yellow. |
Odour/taste |
A strong, unpleasant odour; no distinctive
taste. |
Habitat & Ecological role |
In Britain and Ireland the Dune Stinkhorn is confined almost exclusively to sand dunes, but in many other countries it occurs also in dry inland habitats. |
Season |
June to October in Britain and Ireland. |
Similar species |
Phallus impudicus, the Stinkhorn, has a white volva and is typically somewhat taller than the Dune Stinkhorn. |
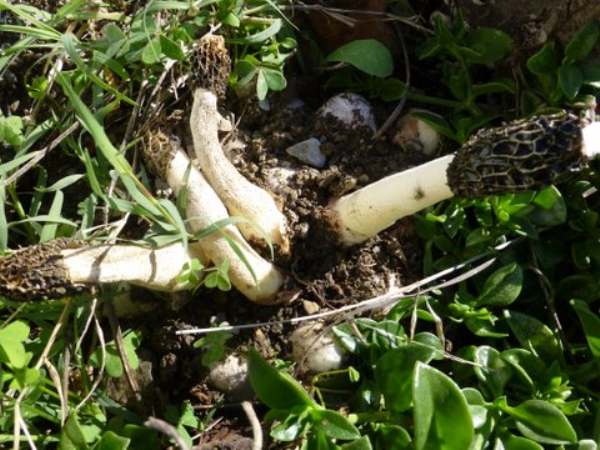

The picture shown above was kindly contributed by Katherine Paterson and shows a large group of stinkhorns and several more eggs yet to 'hatch' (species not determined) in Andalucia, southern Spain.
Reference Sources
Fascinated by Fungi, 2nd Edition, Pat O'Reilly 2016, reprinted by Coch-y-bonddu Books in 2022.
Persoon C H (1801). Systema Methodica Fungorum. Göttingen: Apud H. Dieterich. p. 246.
Pegler, D N, Laessoe, T & Spooner, B M (1995). British Puffballs, Earthstars and Stinkhorns. Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew.
Dictionary of the Fungi; Paul M. Kirk, Paul F. Cannon, David W. Minter and J. A. Stalpers; CABI, 2008
Taxonomic history and synonym information on these pages is drawn from many sources but in particular from the British Mycological Society's GB Checklist of Fungi.
Top of page...
Fascinated by Fungi. Back by popular demand, Pat O'Reilly's best-selling 450-page hardback book is available now. The latest second edition was republished with a sparkling new cover design in September 2022 by Coch-y-Bonddu Books. Full details and copies are available from the publisher's online bookshop...